By Martin North, cross-posted from the Digital Finance Analytics Blog:
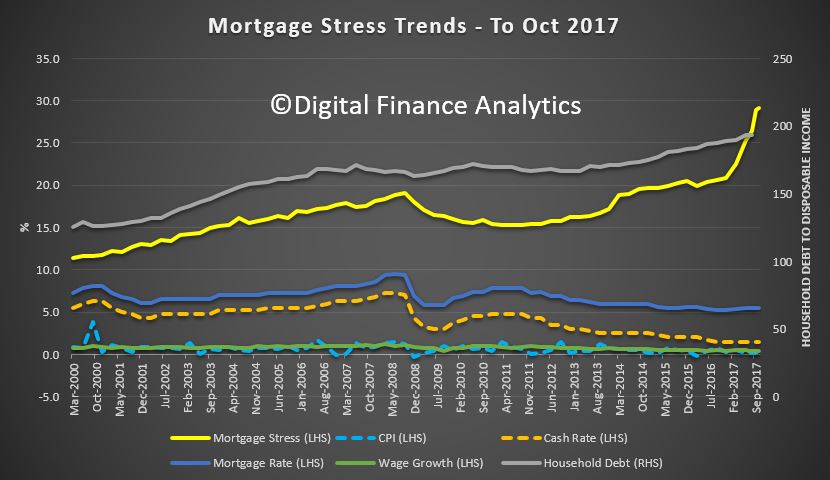
Digital Finance Analytics has released the October 2017 Mortgage Stress and Default Analysis update. Across Australia, more than 910,000 households are estimated to be now in mortgage stress (last month 905,000) and more than 21,000 of these in severe stress, up by 3,000 from last month. This equates to 29.2% of households. We see continued default pressure building in Western Australia, as well as among more affluent households, beyond the traditional mortgage belts across the country.
 We estimate that more than 52,000 households risk 30-day default in the next 12 months, up 3,000 from last month. We expect bank portfolio losses to be around 2.8 basis points ahead, though with losses in WA rising to 4.9 basis points.
We estimate that more than 52,000 households risk 30-day default in the next 12 months, up 3,000 from last month. We expect bank portfolio losses to be around 2.8 basis points ahead, though with losses in WA rising to 4.9 basis points. Risks in the system continue to rise, and while recent strengthening of lending standards will help protect new borrowers, there are many households currently holding loans which would not now be approved. As continued pressure from low wage growth and rising costs bites, those with larger mortgages are having more difficulty balancing the family budget. These stressed households are less likely to spend at the shops, which will act as a further drag anchor on future growth, one reason why retail spending is muted. The number of households impacted are economically significant, especially as household debt continues to climb to new record levels. Mortgage lending is still growing at three times income. This is not sustainable.
Our analysis uses the DFA core market model which combines information from our 52,000 household surveys, public data from the RBA, ABS and APRA; and private data from lenders and aggregators. The data is current to end October 2017. We analyse household cash flow based on real incomes, outgoings and mortgage repayments, rather than using an arbitrary 30% of income.
Households are defined as “stressed” when net income (or cash flow) does not cover ongoing costs. Households in mild stress have little leeway in their cash flows, whereas those in severe stress are unable to meet repayments from current income. In both cases, households manage this deficit by cutting back on spending, putting more on credit cards and seeking to refinance, restructure or sell their home. Those in severe stress are more likely to be seeking hardship assistance and are often forced to sell.
The forces which are lifting mortgage stress levels remain largely the same. In cash flow terms, we see households having to cope with rising living costs whilst real incomes continue to fall and underemployment remains high. Households have larger mortgages, thanks to the strong rise in home prices, especially in the main eastern state centres. While mortgage rates remain quite low for owner occupied borrowers, those with interest only loans or investment loans have seen significant rises. We expect some upward pressure on real mortgage rates in the next year as international funding pressures mount, a potential for local rate rises and margin pressure on the banks. We revised our expectation of potential interest rate rises, given the stronger data on the global economy.
Probability of default extends our mortgage stress analysis by overlaying economic indicators such as employment, future wage growth and cpi changes. We have also extended our Core Market Model to examine the potential of 90-Day defaults (PD90) and portfolio risk of loss in basis point and value terms. Losses (in terms of value) are likely to be higher among more affluent households.

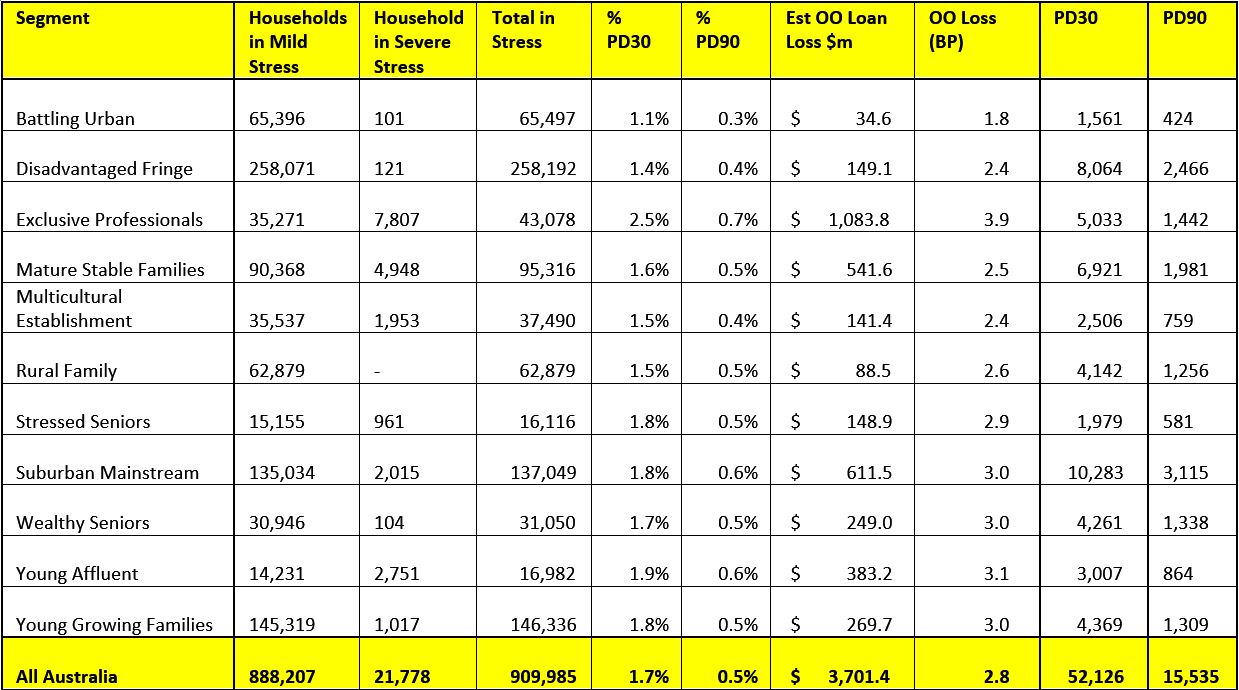 Regional analysis shows that NSW has 242,399 households in stress (238,703 last month), VIC 250,259 (243,752 last month), QLD 162,726 (168,051 last month) and WA 121,393 (124,754 last month). The probability of default rose, with around 9,800 in WA, around 9,600 in QLD, 13,000 in VIC and 13,900 in NSW.
Regional analysis shows that NSW has 242,399 households in stress (238,703 last month), VIC 250,259 (243,752 last month), QLD 162,726 (168,051 last month) and WA 121,393 (124,754 last month). The probability of default rose, with around 9,800 in WA, around 9,600 in QLD, 13,000 in VIC and 13,900 in NSW.
